Famotidine for Toddlers: Understanding Usage, Dosage, and Safety
As parents, ensuring the health and well-being of our toddlers is paramount. When digestive issues arise, such as acid reflux or GERD, healthcare providers may prescribe famotidine. This article provides a comprehensive overview of famotidine for toddlers, covering its uses, appropriate dosage, potential side effects, and crucial safety considerations. Understanding these aspects will empower you to make informed decisions regarding your child’s health. We aim to present the information clearly and concisely, drawing on medical expertise and current research to provide a reliable resource for parents navigating this topic.
What is Famotidine?
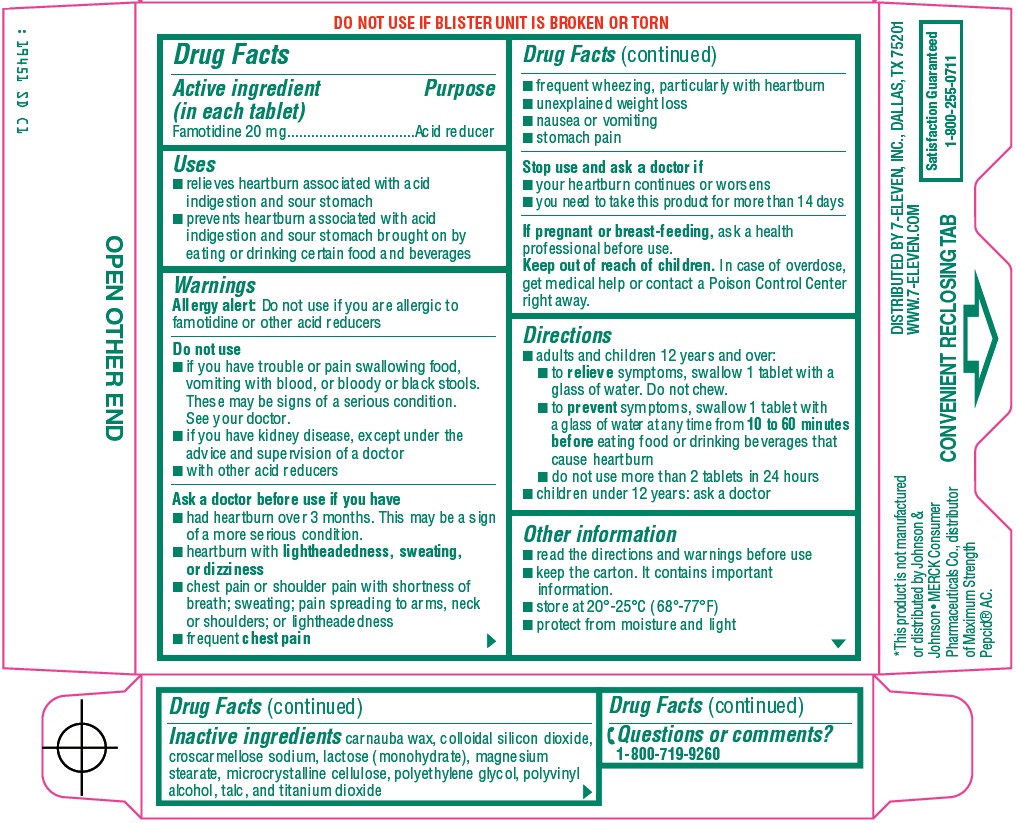
Famotidine is a histamine-2 receptor antagonist (H2 blocker). This means it works by reducing the amount of acid produced by the stomach. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Peptic ulcers
- Esophagitis
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
While primarily used in adults, famotidine can be prescribed off-label for infants and toddlers under specific circumstances. It’s crucial to understand that “off-label” use means the medication is being used for a condition or age group that it has not been specifically approved for by regulatory agencies like the FDA. However, it does not mean the use is unsafe or ineffective; it simply means that additional clinical judgment is required. Always follow your pediatrician’s instructions carefully.
Why Might a Toddler Need Famotidine?
Famotidine for toddlers is typically prescribed when they experience persistent symptoms of acid reflux or GERD. These symptoms may include:
- Frequent spitting up or vomiting
- Irritability, especially after feeding
- Poor weight gain or weight loss
- Refusal to eat
- Coughing or wheezing
- Arching of the back during or after feeding
- Sleep disturbances
It’s important to distinguish between normal infant reflux (which is common and usually resolves on its own) and GERD, which is a more severe and persistent condition that requires medical intervention. A pediatrician will conduct a thorough evaluation to determine if famotidine is the appropriate treatment option.
Dosage and Administration of Famotidine for Toddlers
The dosage of famotidine for toddlers is determined by their weight and the severity of their condition. It is essential to strictly adhere to the dosage prescribed by the pediatrician. Never adjust the dosage on your own.
Famotidine is available in several forms, including:
- Oral suspension (liquid)
- Tablets
- Orally disintegrating tablets
For toddlers, the oral suspension is often the preferred form due to ease of administration. If tablets are prescribed, they may need to be crushed and mixed with a small amount of food or liquid. Always consult with your pharmacist to ensure the tablet can be safely crushed and that it will not affect the medication’s efficacy.
Administer famotidine as directed, usually once or twice daily. It is often recommended to give it before meals to maximize its effectiveness in reducing stomach acid production. Use a calibrated measuring device (such as a syringe or medicine cup) to ensure accurate dosing. Never use a household spoon, as it may not provide an accurate measurement.
If a dose is missed, administer it as soon as you remember, unless it is close to the time for the next dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and continue with the regular dosing schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up.
Potential Side Effects of Famotidine in Toddlers
Like all medications, famotidine can cause side effects. While most toddlers tolerate famotidine well, it’s important to be aware of potential adverse reactions. Common side effects may include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
Less common but more serious side effects may include:
- Allergic reactions (rash, hives, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing)
- Irregular heartbeat
- Seizures
- Liver problems (yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, pale stools)
If your toddler experiences any concerning side effects, contact your pediatrician immediately. Allergic reactions require immediate medical attention.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
Before starting famotidine, inform your pediatrician about your toddler’s medical history, including any allergies, existing medical conditions, and other medications they are taking. This information is crucial to prevent potential drug interactions and ensure the safe use of famotidine.
Famotidine can interact with certain medications, such as:
- Antacids (may decrease the absorption of famotidine)
- Certain antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole)
- Medications that require an acidic environment for absorption
To minimize the risk of interactions with antacids, administer famotidine at least one to two hours before or after giving antacids.
Store famotidine at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct sunlight. Keep it out of reach of children. Check the expiration date before administering the medication, and dispose of any expired or unused medication properly.
Alternative Treatments for Toddler Reflux
While famotidine can be effective in treating GERD in toddlers, it’s important to explore other management strategies as well. These may include:
- Dietary modifications: For formula-fed toddlers, consider using a thickened formula or a hypoallergenic formula if a milk protein allergy is suspected. For toddlers eating solid foods, avoid trigger foods such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, and caffeine.
- Positioning: Keep your toddler upright for at least 30 minutes after feeding. Avoid placing them in a car seat or swing immediately after eating.
- Smaller, more frequent feedings: This can help reduce the amount of pressure on the stomach.
- Elevating the head of the crib: This can help reduce reflux during sleep.
In some cases, a pediatrician may recommend a different medication, such as a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), if famotidine is not effective. However, PPIs are generally reserved for more severe cases of GERD due to their potential for long-term side effects.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult your pediatrician if your toddler experiences any of the following:
- Worsening symptoms of reflux or GERD
- New or concerning symptoms
- Lack of improvement with famotidine treatment
- Signs of dehydration (decreased urination, dry mouth, sunken eyes)
- Blood in vomit or stool
It is crucial to have open communication with your pediatrician to address any concerns and ensure the best possible care for your toddler.
Conclusion
Famotidine for toddlers can be a valuable tool in managing acid reflux and GERD. However, it is essential to use it judiciously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. By understanding the uses, dosage, potential side effects, and safety considerations of famotidine, parents can make informed decisions and work collaboratively with their pediatrician to ensure the health and well-being of their toddlers. Remember that lifestyle modifications and other treatment options may also play a crucial role in managing reflux symptoms. Always prioritize open communication with your pediatrician to address any concerns and ensure the best possible care for your child. If prescribed, ensure the proper dosage and administration of famotidine for your young child. Always keep the medication out of reach of children.
[See also: Understanding Infant Reflux and GERD]
[See also: Safe Medication Practices for Toddlers]
[See also: Managing Toddler Digestive Issues Naturally]
