I Need Additional Permissions to Hand Out All the Roles: A Comprehensive Guide
Ever found yourself in a situation where you need to assign roles within a system, only to be met with a frustrating “Access Denied” message? The need for additional permissions to hand out all the roles is a common challenge in many organizations, regardless of size or industry. This article delves into the intricacies of role-based access control (RBAC), exploring why this issue arises, how to diagnose it, and the steps you can take to resolve it. We’ll cover everything from understanding the fundamental principles of RBAC to practical solutions for granting the necessary authorizations. Getting the right permissions is crucial for maintaining security, efficiency, and accountability within your organization.
Understanding Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
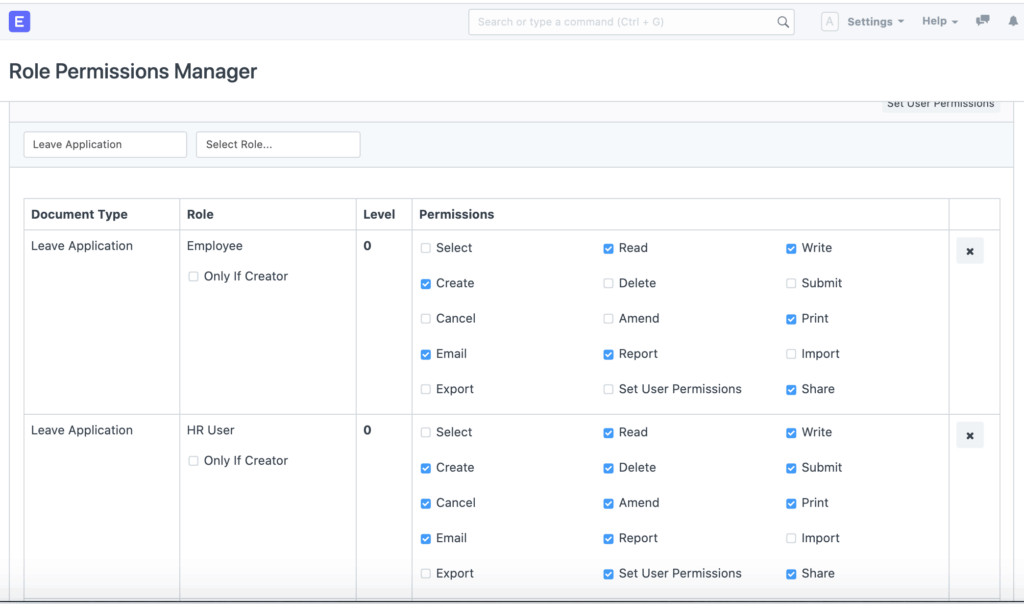
Before diving into the specifics of needing additional permissions to hand out all the roles, it’s essential to understand the underlying principles of RBAC. RBAC is a security mechanism that restricts system access to authorized users. It’s a policy-neutral access control mechanism defined around roles and privileges. Essentially, users are assigned to specific roles, and these roles are granted the necessary permissions to perform certain tasks. This approach simplifies access management compared to assigning permissions directly to individual users.
The core components of RBAC include:
- Users: Individuals who interact with the system.
- Roles: Collections of permissions that define what a user can do within the system. Examples include ‘Administrator,’ ‘Editor,’ ‘Viewer,’ etc.
- Permissions: Specific authorizations to perform actions, such as reading data, creating new records, or deleting files.
- Assignments: The mapping of users to roles.
When a user attempts to perform an action, the system checks their assigned roles and the associated permissions. If the user’s roles grant the necessary permission, the action is allowed. Otherwise, access is denied. This structured approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and simplifies the process of managing user privileges.
Why Do I Need Additional Permissions to Hand Out All the Roles?
The need for additional permissions to hand out all the roles typically arises due to limitations in your current user account’s privileges. Here are several common reasons:
- Insufficient Privileges: Your account may not have the necessary authorization to modify role assignments. This is the most common reason.
- Role Hierarchy: Some systems implement a role hierarchy, where higher-level roles can manage lower-level roles, but not the other way around. If the role you’re trying to assign is higher than your own, you’ll need elevated permissions.
- Security Restrictions: Security policies may restrict certain role assignments to specific users or groups to prevent unauthorized privilege escalation.
- System Configuration: The system might be configured to require explicit approval from a higher authority before certain roles can be assigned.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): In some cases, assigning highly privileged roles may require MFA to ensure the user making the change is who they claim to be. This adds an extra layer of security.
Understanding the specific reason why you need additional permissions to hand out all the roles is crucial for finding the right solution. It often involves checking your current permissions, the role hierarchy, and the system’s security policies.
Diagnosing the Issue: Identifying the Root Cause
Before requesting additional permissions to hand out all the roles, it’s essential to diagnose the issue thoroughly. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Check Your Current Permissions: Most systems provide a way to view your account’s current roles and permissions. Review these to ensure you have the necessary privileges to manage role assignments.
- Examine the Role Hierarchy: If your system uses a role hierarchy, determine the relationship between your role and the role you’re trying to assign. If the target role is higher in the hierarchy, you’ll likely need elevated permissions.
- Review Security Policies: Consult your organization’s security policies to understand any restrictions on role assignments. These policies may outline specific requirements or approval processes for assigning certain roles.
- Check System Logs: System logs can provide valuable insights into why your role assignment attempt failed. Look for error messages or audit trails that indicate permission issues.
- Consult Documentation: Review the system’s documentation for guidance on role management and permission requirements. The documentation may contain specific instructions or troubleshooting tips.
By following these steps, you can pinpoint the exact reason why you need additional permissions to hand out all the roles and gather the necessary information to request the appropriate authorizations.
Solutions: How to Obtain the Necessary Permissions
Once you’ve diagnosed the issue, you can take steps to obtain the necessary additional permissions to hand out all the roles. Here are several possible solutions:
- Request Elevated Privileges: The most common solution is to request elevated privileges from your system administrator or security officer. Clearly explain why you need the permissions and provide evidence to support your request.
- Delegate Authority: If you only need to assign roles temporarily, you can request a temporary delegation of authority from a user who already has the necessary permissions. This allows you to perform the role assignments without permanently changing your own privileges.
- Modify Role Assignments: In some cases, the issue may be that the roles themselves are not properly configured. You can work with your system administrator to modify the role assignments to grant the necessary permissions.
- Implement a Workflow: For sensitive role assignments, you can implement a workflow that requires approval from multiple stakeholders. This ensures that all role assignments are properly vetted and authorized.
- Automate Role Management: Consider automating role management using identity and access management (IAM) tools. These tools can streamline the process of requesting and granting permissions, reducing the risk of errors and delays.
When requesting additional permissions to hand out all the roles, it’s important to be clear, concise, and professional. Explain the business need for the permissions and provide any relevant documentation or justification. Be prepared to answer questions about your request and to provide additional information if needed.
Best Practices for Managing Role-Based Access Control
To avoid frequent requests for additional permissions to hand out all the roles, it’s essential to implement best practices for managing RBAC. Here are some key recommendations:
- Regularly Review Role Assignments: Periodically review role assignments to ensure they are still appropriate and necessary. Remove any unnecessary permissions to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- Enforce the Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users only the minimum permissions they need to perform their job duties. This minimizes the potential impact of a security breach.
- Implement Strong Authentication: Use strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to protect against unauthorized access.
- Monitor System Activity: Monitor system activity for suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts. Implement alerting mechanisms to notify administrators of potential security incidents.
- Provide Training: Provide training to users on RBAC principles and best practices. This helps them understand their responsibilities and avoid making mistakes that could compromise security.
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed documentation of all roles, permissions, and assignments. This makes it easier to manage RBAC and troubleshoot issues.
By following these best practices, you can improve the security and efficiency of your RBAC system and reduce the need for frequent requests for additional permissions to hand out all the roles. A well-managed RBAC system is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
The Future of Role-Based Access Control
The field of RBAC is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches emerging to address the changing security landscape. Some of the key trends in RBAC include:
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): ABAC is a more granular approach to access control that uses attributes to determine access rights. Attributes can include user attributes (e.g., job title, department), resource attributes (e.g., file type, sensitivity level), and environmental attributes (e.g., time of day, location).
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Access: JIT access grants users temporary permissions only when they are needed. This reduces the risk of long-term privilege creep and minimizes the potential impact of a security breach.
- Zero Trust Security: Zero trust security is a security model that assumes no user or device is trusted by default. All access requests are verified, regardless of whether they originate from inside or outside the network.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML can be used to automate RBAC management, detect anomalies, and predict potential security risks.
As these technologies mature, they are likely to have a significant impact on the way RBAC is implemented and managed. Organizations that embrace these trends will be better positioned to protect their data and systems from evolving threats. Staying informed about the latest developments in RBAC is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture and minimizing the need for constant requests for additional permissions to hand out all the roles.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of RBAC and understanding why you need additional permissions to hand out all the roles can be challenging. However, by understanding the principles of RBAC, diagnosing the issue effectively, and implementing appropriate solutions, you can ensure that your organization’s access control system is secure, efficient, and compliant. Remember to follow best practices for managing RBAC and stay informed about the latest trends in the field to maintain a strong security posture and minimize the need for frequent permission requests. In the end, a well-managed RBAC system empowers your organization to operate securely and efficiently, allowing users to access the resources they need while protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. [See also: Understanding Role Hierarchy in Access Control] [See also: Implementing Least Privilege Access] [See also: Best Practices for IAM]
