The Ultimate Guide to Bonding Acrylic to Metal: Techniques, Adhesives, and Best Practices
Bonding acrylic to metal presents a unique set of challenges, demanding careful consideration of material properties, adhesive selection, and application techniques. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of achieving strong, durable bonds between these dissimilar materials, providing insights into the best practices for ensuring long-term performance. Whether you’re working on industrial applications, artistic projects, or DIY endeavors, understanding the nuances of bonding acrylic to metal is crucial for success. Let’s delve into the methods, materials, and considerations necessary for a robust and lasting bond.
Understanding the Challenges of Bonding Acrylic to Metal
The primary challenge in bonding acrylic to metal lies in their differing thermal expansion coefficients. Acrylic expands and contracts significantly more than most metals with temperature changes. This difference can induce stress at the bond line, potentially leading to failure over time. Furthermore, the surfaces of acrylic and metal possess distinct properties that affect adhesion. Acrylic is generally smooth and non-porous, while metals often have varied surface textures and may be prone to oxidation. Therefore, proper surface preparation and adhesive selection are paramount.
Surface Preparation: The Foundation of a Strong Bond
Effective surface preparation is arguably the most critical step in bonding acrylic to metal. Contaminants such as oils, grease, and dust can impede adhesion and compromise the bond’s integrity. The following steps outline a comprehensive surface preparation process:
- Cleaning: Begin by thoroughly cleaning both the acrylic and metal surfaces. Use a suitable solvent, such as isopropyl alcohol or a specialized degreaser, to remove any surface contaminants. Ensure the solvent is compatible with both materials and does not leave any residue.
- Abrading (Metal): For metal surfaces, light abrasion can significantly improve adhesion. Use fine-grit sandpaper or a Scotch-Brite pad to create a slightly roughened surface. This increases the surface area available for bonding and promotes mechanical interlocking with the adhesive.
- Priming (Optional): In some cases, applying a primer to the metal surface can enhance adhesion. Primers create a chemical bridge between the metal and the adhesive, improving bond strength and durability. Consult the adhesive manufacturer’s recommendations to determine if a primer is necessary.
- Drying: After cleaning and abrading, allow both surfaces to dry completely before applying the adhesive. Any residual moisture can interfere with the bonding process and weaken the bond.
Choosing the Right Adhesive for Bonding Acrylic to Metal
Selecting the appropriate adhesive is crucial for achieving a strong and durable bond between acrylic and metal. Several types of adhesives are suitable for this application, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the most common options:
Acrylic Adhesives
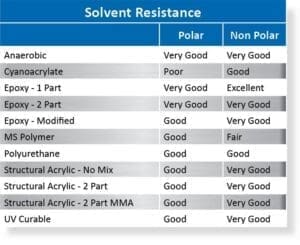
Acrylic adhesives are specifically designed for bonding acrylic materials. They offer excellent adhesion to acrylic and can also bond well to certain metals. These adhesives typically provide good resistance to UV light and weathering, making them suitable for outdoor applications. However, they may not be as strong as other adhesive types for bonding to all metals.
Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives are known for their high strength and excellent adhesion to a wide range of materials, including acrylic and metal. They offer good resistance to chemicals, heat, and moisture, making them suitable for demanding applications. Epoxy adhesives typically require mixing two components before application and have a longer curing time than other adhesive types. They are a robust choice for bonding acrylic to metal in structural applications.
Polyurethane Adhesives
Polyurethane adhesives offer good flexibility and impact resistance, making them suitable for applications where the bond may be subjected to vibration or stress. They also provide good adhesion to both acrylic and metal. However, they may not be as resistant to UV light and chemicals as epoxy adhesives. Polyurethane adhesives are a good option for bonding acrylic to metal in applications where flexibility is important.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (Super Glue)
Cyanoacrylate adhesives, commonly known as super glue, are fast-curing adhesives that can bond acrylic to metal. However, they typically provide a brittle bond with limited resistance to impact and vibration. They are best suited for small-scale applications where high strength is not required. While convenient for quick fixes, they are generally not recommended for critical bonding acrylic to metal applications.
Structural Acrylic Adhesives
These are modified acrylic adhesives designed for high-performance bonding. They offer improved strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors compared to standard acrylic adhesives. Structural acrylics often require minimal surface preparation and can bond to a variety of metals. They are a strong contender for bonding acrylic to metal when long-term reliability is essential.
Application Techniques for Bonding Acrylic to Metal
Proper application techniques are crucial for achieving a strong and durable bond. The following guidelines outline the key steps for applying adhesive:
- Apply Adhesive: Apply a thin, even layer of adhesive to one or both surfaces to be bonded. Follow the adhesive manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate amount of adhesive to use. Avoid applying too much adhesive, as this can weaken the bond.
- Assemble Parts: Carefully align the acrylic and metal parts and bring them together. Apply gentle pressure to ensure good contact between the surfaces.
- Clamping (If Necessary): If necessary, use clamps or weights to hold the parts in place during the curing process. This ensures that the adhesive maintains good contact with both surfaces and prevents movement that could weaken the bond.
- Curing: Allow the adhesive to cure according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Curing times can vary depending on the type of adhesive used. Do not disturb the parts during the curing process.
- Post-Curing (Optional): Some adhesives may benefit from post-curing, which involves exposing the bonded parts to heat or UV light after the initial curing process. This can further strengthen the bond and improve its resistance to environmental factors.
Considerations for Long-Term Performance When Bonding Acrylic to Metal
To ensure long-term performance, consider the following factors when bonding acrylic to metal:
- Thermal Expansion: Account for the difference in thermal expansion coefficients between acrylic and metal. Choose an adhesive that can accommodate this difference without causing stress at the bond line. Flexible adhesives, such as polyurethane, can be a good choice.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the environmental conditions to which the bonded parts will be exposed. Select an adhesive that is resistant to UV light, moisture, chemicals, and other environmental factors.
- Load Requirements: Determine the load requirements of the bond. Choose an adhesive that is strong enough to withstand the anticipated loads without failing. Epoxy adhesives are often a good choice for high-load applications.
- Surface Compatibility: Ensure that the adhesive is compatible with both the acrylic and metal surfaces. Some adhesives may not bond well to certain types of metal or acrylic.
- Testing: Perform testing to verify the strength and durability of the bond. This can involve subjecting the bonded parts to simulated environmental conditions and load testing.
Troubleshooting Common Issues When Bonding Acrylic to Metal
Even with careful planning and execution, issues can sometimes arise when bonding acrylic to metal. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Weak Bond: A weak bond can be caused by inadequate surface preparation, incorrect adhesive selection, or improper application techniques. Review the surface preparation process, adhesive selection criteria, and application guidelines to identify and correct any issues.
- Bond Failure: Bond failure can occur due to excessive stress, environmental exposure, or adhesive degradation. Re-evaluate the load requirements, environmental conditions, and adhesive properties to ensure that the bond is adequate for the application.
- Bubbles or Voids: Bubbles or voids in the adhesive can weaken the bond. Ensure that the adhesive is applied evenly and that air is not trapped between the surfaces. Use a vacuum chamber to remove air bubbles from the adhesive before application.
- Discoloration: Some adhesives can cause discoloration of the acrylic or metal. Choose an adhesive that is known to be compatible with both materials and does not cause discoloration.
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Bonding Acrylic to Metal
Several industries successfully employ bonding acrylic to metal in various applications. Here are a few examples:
- Aerospace: Acrylic windows are often bonded to metal frames in aircraft. High-strength epoxy adhesives are used to ensure the bond can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures.
- Automotive: Acrylic lenses and reflectors are bonded to metal housings in automotive lighting systems. UV-resistant acrylic adhesives are used to prevent degradation from sunlight exposure.
- Signage: Acrylic lettering and graphics are bonded to metal backings in signage applications. A variety of adhesives, including acrylic and polyurethane, are used depending on the specific requirements.
- Electronics: Acrylic displays are bonded to metal enclosures in electronic devices. Electrically conductive adhesives are sometimes used to provide grounding and shielding.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Bonding Acrylic to Metal
Bonding acrylic to metal requires a thorough understanding of material properties, adhesive selection, and application techniques. By following the guidelines outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can achieve strong, durable bonds that withstand the test of time. Remember to prioritize surface preparation, choose the right adhesive for your specific application, and carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions. With the right approach, you can confidently tackle any project that involves bonding acrylic to metal. Always research and consider [See also: Different Types of Adhesives for Plastics] and [See also: Metal Surface Treatments for Bonding] before starting your project. The key is selecting the right materials and methods for long-lasting success in bonding acrylic to metal.
