What Size Drill Bit Do I Need for a 10-32 Tap? A Comprehensive Guide
Tapping threads into a hole is a common practice in manufacturing, engineering, and even DIY projects. One of the most crucial steps in this process is selecting the correct drill bit size. Using the wrong size can lead to weak threads, broken taps, or even damage to the workpiece. If you’re working with a 10-32 tap, knowing the right drill bit size is essential. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know to ensure a successful tapping operation. Understanding the importance of selecting the right drill bit size for a 10-32 tap will save you time, money, and frustration.
Understanding Thread Tapping
Before diving into the specifics of a 10-32 tap, let’s cover some fundamental concepts of thread tapping. Thread tapping is the process of creating internal threads in a hole, allowing screws or bolts to be securely fastened. The tap itself is a tool with cutting edges that gradually form the threads as it’s turned into the hole.
What is a 10-32 Tap?
The designation “10-32” refers to the size and thread pitch of the tap. The “10” indicates the nominal size of the screw, and “32” specifies the number of threads per inch. Therefore, a 10-32 tap is designed to create threads for a #10 screw with 32 threads per inch.
Why is the Correct Drill Bit Size Important?
Using the correct drill bit size before tapping is critical for several reasons:
- Thread Strength: A properly sized hole ensures that the threads have sufficient material to grip onto, resulting in a strong and reliable connection.
- Tap Life: Drilling the correct size hole reduces the amount of material the tap needs to remove, extending its lifespan and preventing premature wear or breakage.
- Ease of Tapping: A hole that is too small makes tapping difficult and increases the risk of breaking the tap. A hole that is too large results in weak threads.
- Accuracy: Correctly sized holes lead to more accurate and consistent thread formation.
Determining the Correct Drill Bit Size for a 10-32 Tap
So, what size drill bit do you need for a 10-32 tap? The most common method for determining the correct drill bit size involves using a thread chart or a simple formula. Let’s explore both approaches.
Using a Thread Chart
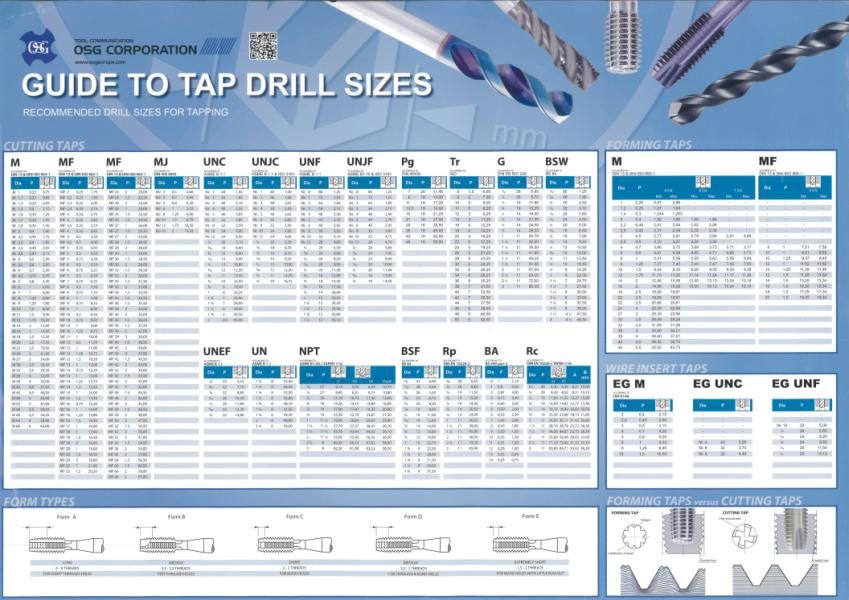
A thread chart is a table that lists the recommended drill bit sizes for various tap sizes. These charts are readily available online or in machinist handbooks. For a 10-32 tap, the thread chart will typically recommend a specific drill bit size. These charts often provide both fractional and metric equivalents.
For a 10-32 tap, a #21 drill bit (0.159 inches) is generally recommended. This size provides the optimal balance between thread strength and ease of tapping. Always double-check the thread chart you are using, as slight variations may exist depending on the source.
Calculating Drill Bit Size Manually
If you don’t have access to a thread chart, you can calculate the drill bit size using a simple formula:
Drill Bit Size = Tap Size – (1 / Threads Per Inch)
For a 10-32 tap:
Drill Bit Size = 0.190 – (1 / 32) = 0.190 – 0.03125 = 0.15875 inches
This calculation suggests a drill bit size of approximately 0.15875 inches, which is very close to the #21 drill bit size (0.159 inches) recommended by thread charts. Note that 0.190 is the major diameter of a #10 screw.
Why the Minor Difference?
The slight difference between the calculated value and the chart recommendation is due to the desired thread engagement. A 75% thread engagement is commonly targeted, as it provides a good balance between strength and ease of tapping. The formula above provides a close approximation, but thread charts often incorporate slight adjustments based on empirical data and industry standards.
Choosing the Right Drill Bit Material
The material of the drill bit is another important consideration. Different materials are better suited for different types of workpieces. Here are some common drill bit materials:
- High-Speed Steel (HSS): HSS drill bits are versatile and suitable for drilling into a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, and plastic.
- Cobalt: Cobalt drill bits are more heat-resistant than HSS bits, making them ideal for drilling into harder materials like stainless steel.
- Carbide: Carbide drill bits are the most durable and heat-resistant, making them suitable for production environments and extremely hard materials.
For most DIY and general-purpose applications involving a 10-32 tap, an HSS drill bit will suffice. However, if you’re working with harder materials, consider using a cobalt or carbide drill bit.
Step-by-Step Guide to Tapping a 10-32 Thread
Now that you know what size drill bit to use for a 10-32 tap, let’s walk through the steps of tapping a thread:
- Prepare the Workpiece: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped and properly aligned.
- Drill the Hole: Using the appropriate drill bit (#21 or 0.159 inches for a 10-32 tap), drill a hole perpendicular to the surface of the workpiece.
- Deburr the Hole: Use a deburring tool or countersink to remove any sharp edges or burrs from the hole. This will help the tap enter the hole smoothly.
- Apply Cutting Fluid: Apply a small amount of cutting fluid to the tap and the hole. Cutting fluid reduces friction, dissipates heat, and helps to create cleaner threads.
- Start Tapping: Align the tap with the hole and apply gentle pressure while turning it clockwise. Use a tap handle or wrench to provide leverage.
- Back Off Periodically: After each full turn, back the tap off by about half a turn. This helps to break the chip and prevent the tap from binding.
- Continue Tapping: Continue tapping until the desired thread depth is reached.
- Clean the Threads: Remove the tap and clean the threads with compressed air or a brush to remove any remaining chips or debris.
Troubleshooting Common Tapping Problems
Even with the correct drill bit size, tapping can sometimes present challenges. Here are some common problems and how to address them:
- Tap Breaking: This can occur if the hole is too small, the tap is forced, or the material is too hard. Ensure you are using the correct drill bit size, applying cutting fluid, and not applying excessive force.
- Stripped Threads: This happens when the hole is too large, or the tap is overtightened. If the threads are stripped, you may need to use a thread repair kit or start over with a new workpiece.
- Difficult Tapping: This can be caused by a lack of lubrication, a dull tap, or a hard material. Apply cutting fluid, use a sharp tap, and consider using a cobalt or carbide tap for harder materials.
- Inconsistent Threads: This can be due to misalignment or inconsistent pressure. Ensure the tap is properly aligned with the hole and apply consistent pressure while turning.
Alternative Methods and Considerations
While the standard method of using a #21 drill bit for a 10-32 tap is generally reliable, there are some alternative methods and considerations to keep in mind.
Using Oversized or Undersized Drill Bits
In some cases, you may want to intentionally use a slightly oversized or undersized drill bit. An oversized drill bit can make tapping easier, especially in harder materials, but it will result in weaker threads. An undersized drill bit will create stronger threads, but it will require more force to tap and increase the risk of breaking the tap. This is generally not recommended unless you have a specific reason to deviate from the standard drill bit size.
Tapping in Different Materials
The ideal drill bit size can also vary slightly depending on the material you are tapping. Softer materials like aluminum may benefit from a slightly smaller drill bit to ensure sufficient thread engagement. Harder materials like stainless steel may require a slightly larger drill bit to reduce the risk of tap breakage. Always consult material-specific tapping guides for the best results.
Using Spiral Flute Taps
Spiral flute taps are designed to push chips ahead of the tap, making them ideal for tapping blind holes (holes that don’t go all the way through the workpiece). When using a spiral flute tap, it’s particularly important to ensure the correct drill bit size to prevent chip buildup and tap breakage.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct drill bit size for a 10-32 tap is crucial for creating strong, reliable threads. By using a thread chart or calculating the drill bit size manually, you can ensure that you’re using the optimal size for your application. Remember to consider the material of the drill bit and the workpiece, and always use cutting fluid to reduce friction and extend the life of your tap. With the right tools and techniques, you can confidently tap 10-32 threads in a variety of materials. [See also: Understanding Tap and Die Sets] By following this guide, you’ll avoid common pitfalls and achieve professional results every time you need to use a 10-32 tap.
